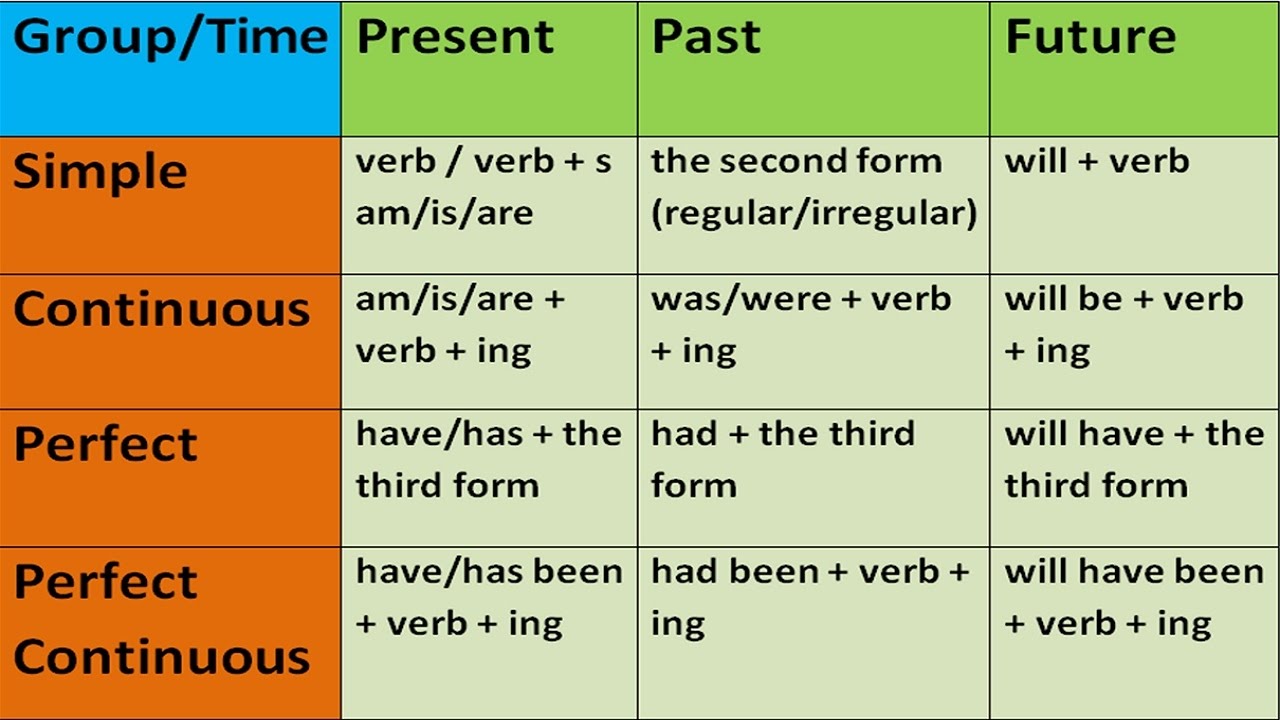
A regular verb forms its verb tenses, especially thepast tenseandpast participle, by adding one in the set of generally accepted standardized suffixes. Regular verbs are conjugated by adding -d, -ed, -ing, or -s to its base form, unlike irregular verbs which have special rules for conjugation. The opposite of a transitive verb is an intransitive verb. A verb is an intransitive verb if it is not used with a direct object. Remember, only nouns, pronouns, and noun phrases can be direct objects.
Prepositional phrases, adjectives, and adverbs cannot be used as direct objects. Once again, both action and stative verbs can be used as intransitive verbs. As stated before, the first person singular form of a regular verb form or to-be verb form is often the same as the simplest form of the verb. However, that's not always true with irregular verbs and words in the to-be form, such as was or were.
This will be discussed later in this guide. Look below to continue learning about the other subject forms and examples of their verb conjugation English use. The future tense is used to express circumstances that will occur in the future.
The future tense is different from the present and past tenses in that there is not usually a type of verb conjugation that shows the future tense. Instead, future verbs are formed by combining them with words like will or shall, or the phrase going to. The different future tenses are simple future, future progressive, future perfect, and future perfect progressive. The future tense is one of the easiest tenses to learn because it has no irregular forms.
Just as its name suggests, it's used to describe actions that will happen in the future. It is formed by combining the helping verb will with the base form of the main verb. The past participle is used for the perfect tenses. In regular verbs, it's the same as the simple past tense, so there's nothing extra to learn. However, irregular verbs often use unique past participles, so you may have to memorize their forms.
Future progressive verbs express actions that will begin in the future and be continuous. In future progressive, the main verb is paired with the future tense of the verb "to be" to show that the action will begin in the future. The progressive form expresses continuous actions that happen over a period of time. They almost always involve some combination of the verb "to be" paired with the main verb ending in -ing.
The main verb can be a present form, a bare infinitive, a past simple form, a past participle or a present participle. Sometimes the auxiliary verb and the main verb are the same. Unlike action verbs, stative verbs refer to conditions or states of being. Generally speaking, we use stative verbs to describe things like qualities, states of existence, opinions, beliefs, and emotions.
When used in a sentence, stative verbs do not refer to actions. It is important to know that some verbs can be used as either action or stative verbs depending on their meaning in the sentence. We are less likely to use stative verbs in the continuous verb tenses.
You will sometimes hear the word participle, which is the form of a verb used with helping verbs to make verb tenses or is used to form adjectives. For instance, breaking and broken are the present and past participles, respectively, of the verb break. A broken dish is an example of a phrase containing a participle as an adjective .
Present progressive verbs express actions that are continuous, and are still happening at the present moment. In present progressive, the main verb is paired with the present tense of the verb "to be" (is/are) to show that the action is happening currently. Simple and perfect verb tenses are also used in forming a progressive verb form that shows us what's taking place at the moment or is continuing.
Add one of the forms of "to be" with the present participle of the verb that ends with –ing. Auxiliary verbs are also known as helping verbs and are used together with a main verb to show the verb's tense or to form a question or negative. Common examples of auxiliary verbs include have, might, will.
These auxiliary verbs give some context to the main verb, for example, letting the reader know when the action took place. Transitive VerbsTransitive verbs are action verbs that always express doable activities that relate or affect someone or something else. In a sentence with a transitive verb, someone or something receives the action of the verb.
When do you use "finishing" versus "to finish" versus "finished"? Helping verbs, also called auxiliary verbs, are helpful verbs that work with other verbs to change the meaning of a sentence. A helping verb combines with a main verb in order to accomplish different goals. These include changing the tense of the verb or altering the mood of a sentence. Auxiliary verbs, or "helping verbs," are used in English to change another verb's tense, voice, or mood. When auxiliary verbs are used, there's always a main verb that represents the main action.
However, the auxiliary verb must still be conjugated correctly. Definitions of the perfect tenses are difficult to understand without examples. Tables 1 and 6 show the regular verb to walk and the irregular verb to be in each of the tenses for first-, second-, and third-person subjects. Regular verbs, like to walk, form the past tense and the perfect tenses by adding -d or -ed to the present tense.
But many English verbs are irregular, forming their past tenses in various ways. Past progressive verbs express actions that began in the past and were continuous, but did not continue into the present. Look at each tense and note how the suffixes change a regular verb form during standard conjugation. For this example, we'll use first person singular form, I. To form other verb tenses, you have to add a form of have, be or will in front of the verb. These are called helping, or auxiliary verbs.
Auxiliary verbs usually accompany the main verb. The main verb provides the main semantic content of the clause. The auxiliary verbs, also helping verbs, are be, do, have, and will. They are used to form compound tenses or the passive voice. For the next little while, we're going to focus on main verbs.
So, forget about those poor little helping verbs for a bit, and let's turn our attention to action verbs and linking verbs. These two kinds of main verbs can act in four different ways. They do not work as verbs in the sentence rather they work as nouns, adjectives, adverbs, etc. Sometimes they become the subject themselves. Verbs in future perfect progressive express a continuous, completed action that will have taken place in the future.
Use "will have been" combined with the -ingform of the main verb. Verb tenses can be difficult to learn in a foreign language. Different cultures think different ways about time.
Chinese, for example, has no grammatical verb tenses. Other languages, like Indonesian, express time only through adverbs — there are no changes to the verb form. The most common linking verb can be found in the various forms of "to be" (am, are, is, was, were, etc.). Sometimes, the forms of "to be" are helping verbs. When an action verb has no direct object, it's called an intransitive verb. An adverb or adverb phrase can follow intransitive verbs, but there will not be a direct object.
Intransitive verbs are action verbs that always express doable activities. They are different from transitive verbs because there is no direct object following an intransitive verb. Our last type of verb isn't actually a verb at all—sorry about that!
However, infinitives look a lot like verbs because they are derived from them. An infinitive of a verb is identical to the base form of the verb. For example, the infinitive form of the verb open is open. Typically, we use infinitives with the word to in order to form infinitive phrases. Infinitive phrases can be used for a variety of reasons, such as to act like nouns, adjectives, or adverbs.
Linking verbs are a special type of stative verb whose name gives a big clue as to what they do. Linking verbs are used to link a subject with a subject complement. A subject complement describes or identifies the subject of the sentence or clause. Linking verbs can function as intransitive verbs, which do not take direct objects. A transitive verb is a verb that is accompanied by a direct object in a sentence.
The direct object is the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that is having something done to it by the subject of the sentence. Both action and stative verbs can have direct objects, which means they can both be used as transitive verbs. Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs. An auxiliary verb extends the main verb by helping to show time, tense, and possibility.
The auxiliary verbs are – be verbs, have, and do. The perfect progressive, just as you would expect, is a combination of the perfect and progressive aspects. Perfect progressive refers to the completed portion of an ongoing action.
It almost always involves a form of the verb "have" and a form of the verb "to be" combined with a verb ending in -ing. You already know quite a lot about how to get verb forms to agree with the subject in a sentence. If you're learning English as a second language, you may wonder about imperfect verb conjugation. Conjugation gives your reader or your listener important background information.
You also saw examples of how you can tell when an action will occur in verb conjugation English tenses. As you can see, among all the subject matches with all the regular verb conjugations the only change occurs with the third person singular form. Here, the verb typically takes an -s suffix. This is the standard pattern with regular verb forms like to work, making this English verb conjugation easy to remember. Let's look at the regular verb to work as an example.
The infinitive form of this action verb is to work. During verb conjugations it will change from the infinitive form depending on the grammatical subject. This means that you add different suffixes to the infinitive form depending on who you're referring to in a sentence. Modals or Modal Verbs or Modal Auxiliary are used to show the mood or attitude of the subject. They are the verbs that are used to indicate modality.
Such as likelihood, ability, permission, request, capacity, suggestions, order, obligation, or advice. Modal verbs always accompany the base form of another verb having semantic content. Modals are the type of auxiliary expressing the subject's mood. They give information about the function of the main verb. A regular word, such as a noun or a verb, has inflections that follow the normal rules.
For instance, the noun cat has a regular plural with -s , and the verb to love forms its tenses in the normal way (loved; loving). Find out more about regular and irregular verbs. Perfect progressive tenses are a combination of perfect and progressive tenses, which show that something began, continued, and ended before another action. The perfect progressive tenses combine the perfect , the progressive and the present participle of the main verb.
What Is Helping Verb In English Grammar Perfect tenses show when an action happened in relation to another action. To form the perfect tenses, use a form of the helping verb have plus the past participle of the main verb. Future perfect continuous tense functions just like the future perfect tense, except with an ongoing action. Both, however, are frequently used with expressions of time. Some verbs in this list can also be action verbs. To figure out if they are linking verbs, you should try replacing them with forms of the be verbs.




























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.